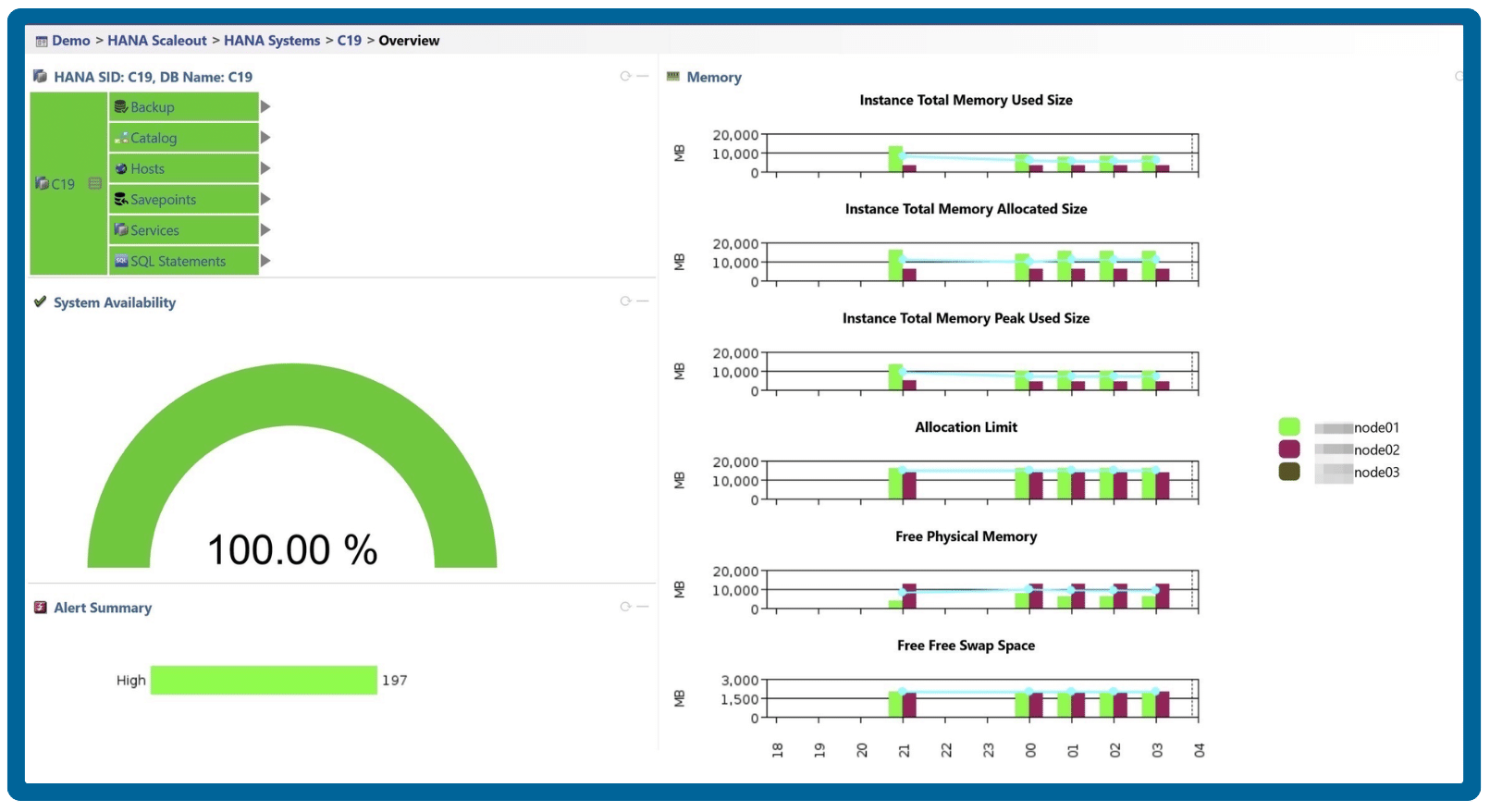
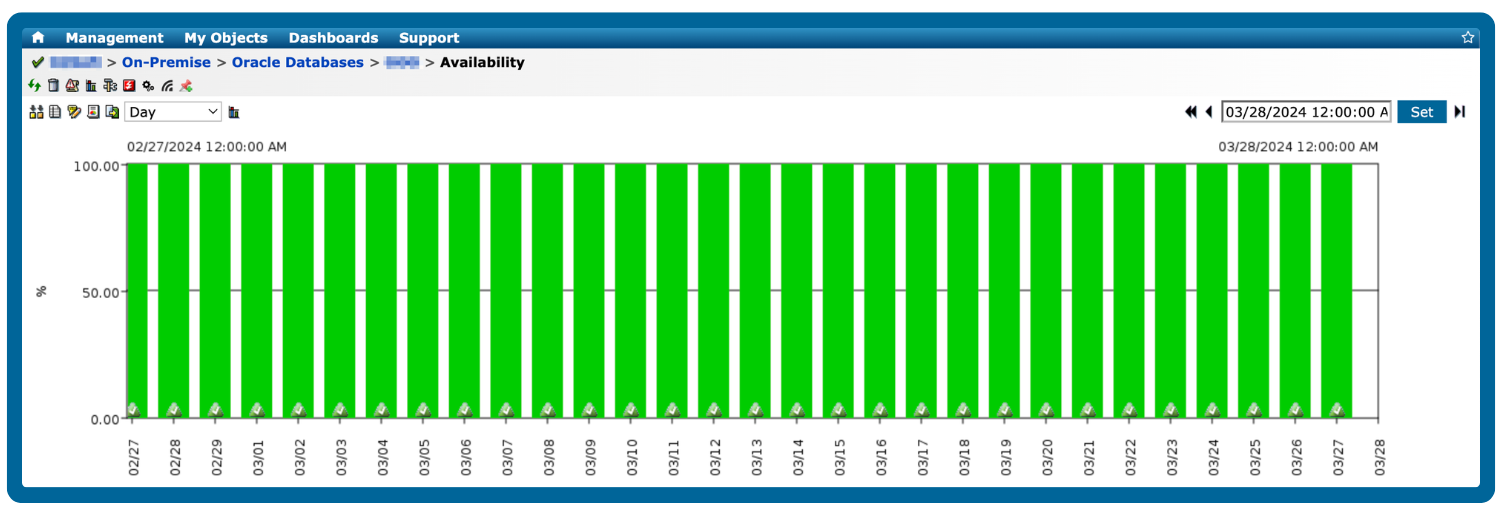
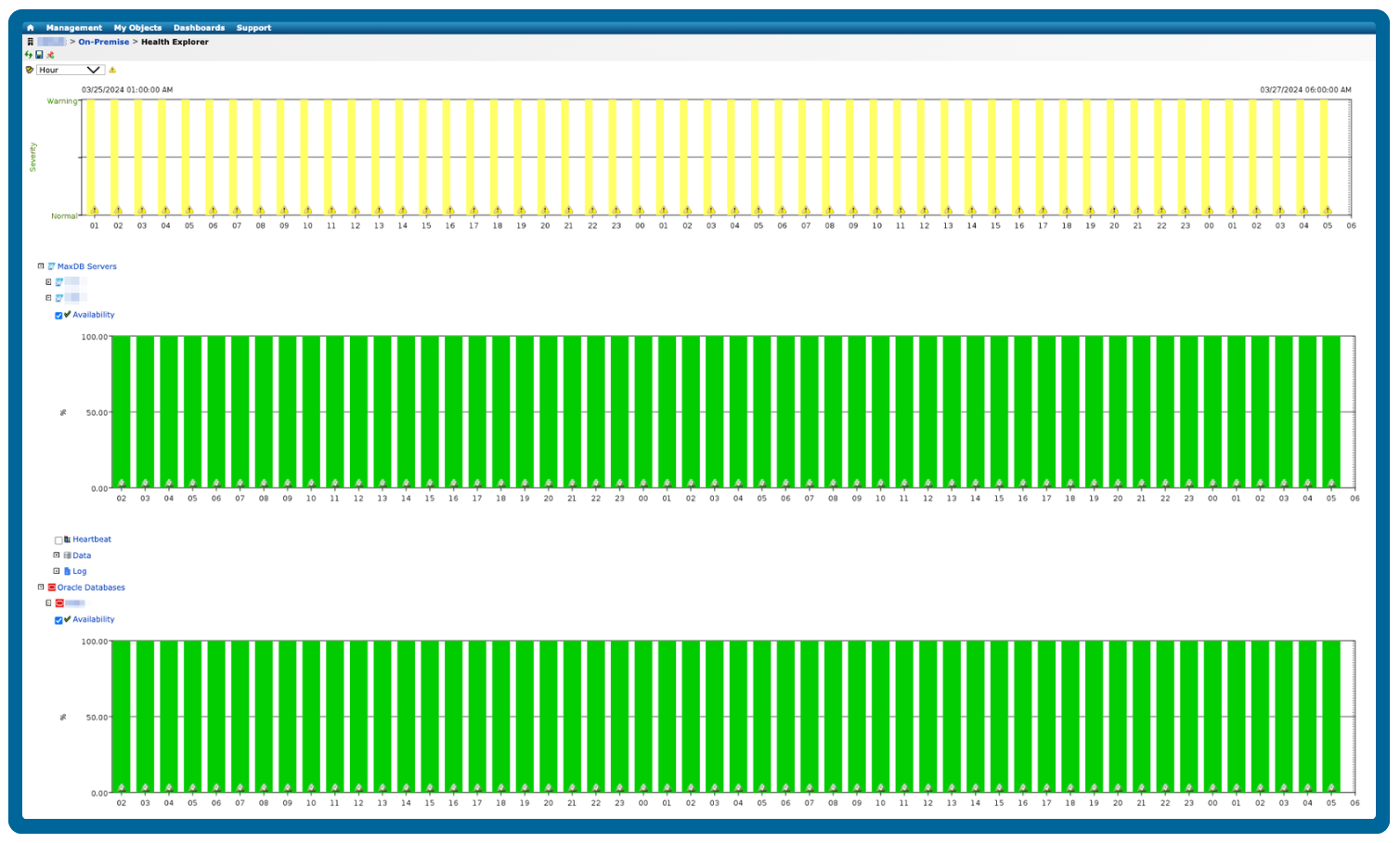
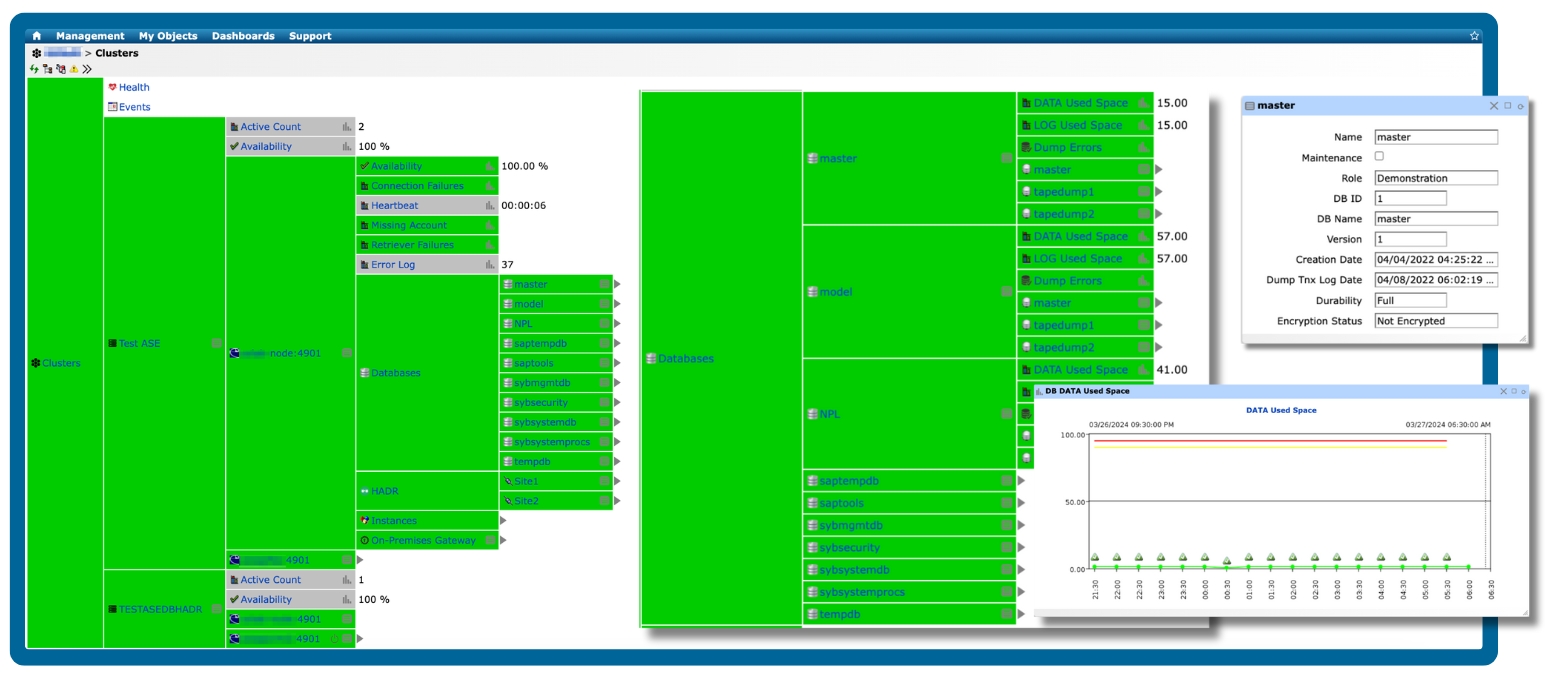
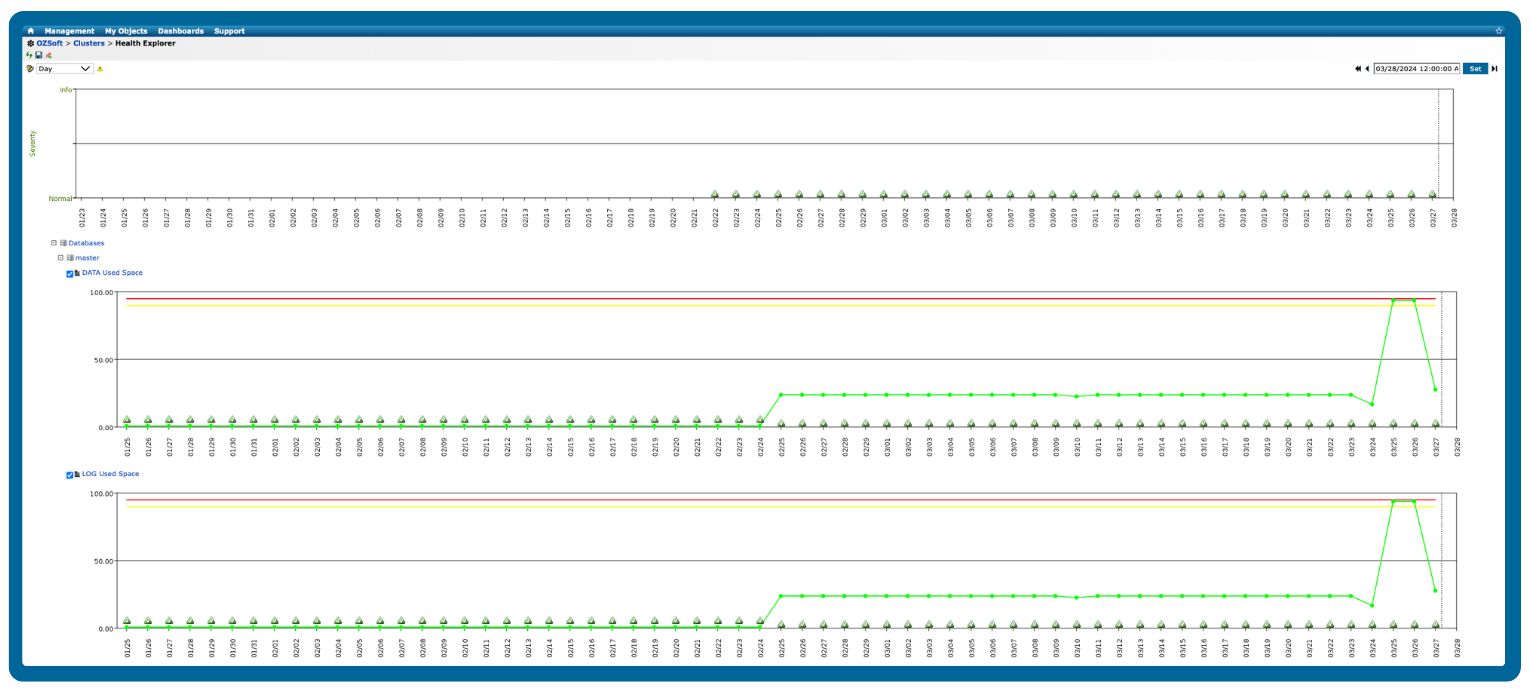
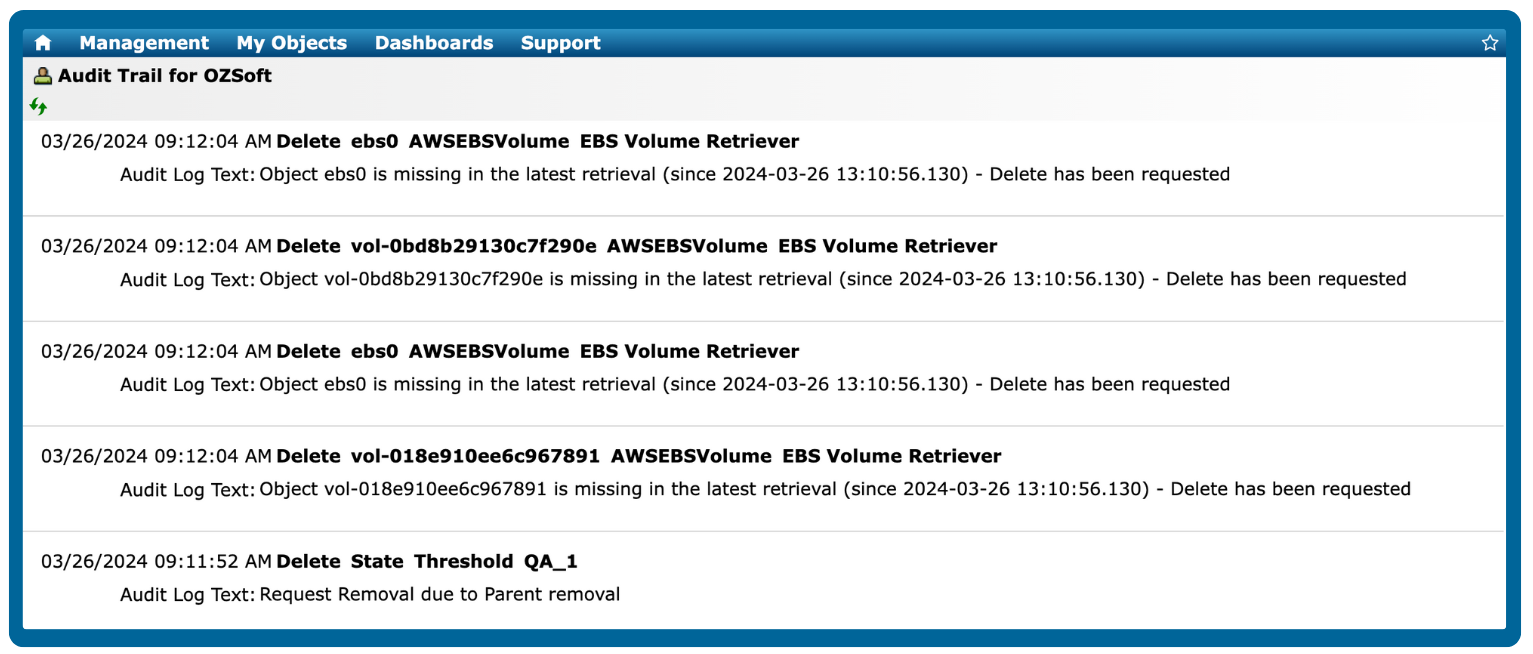
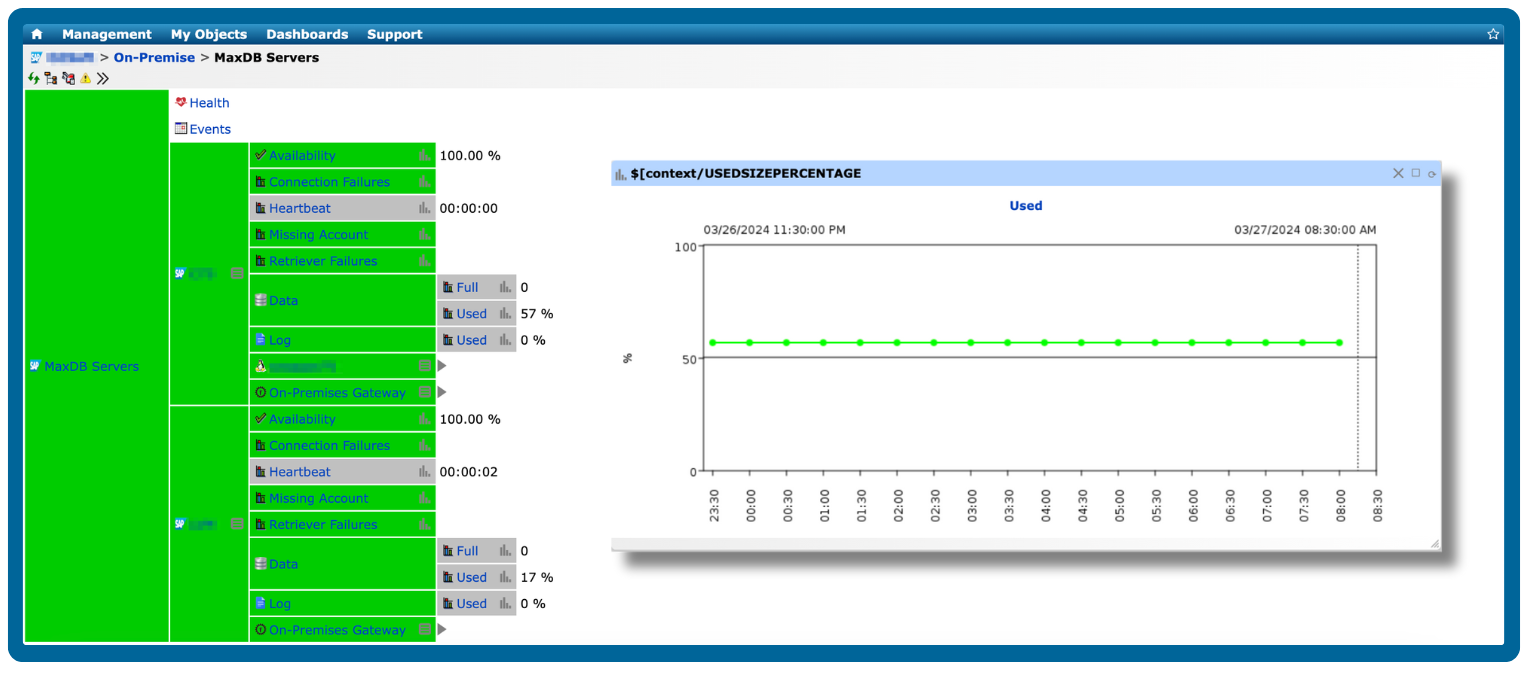
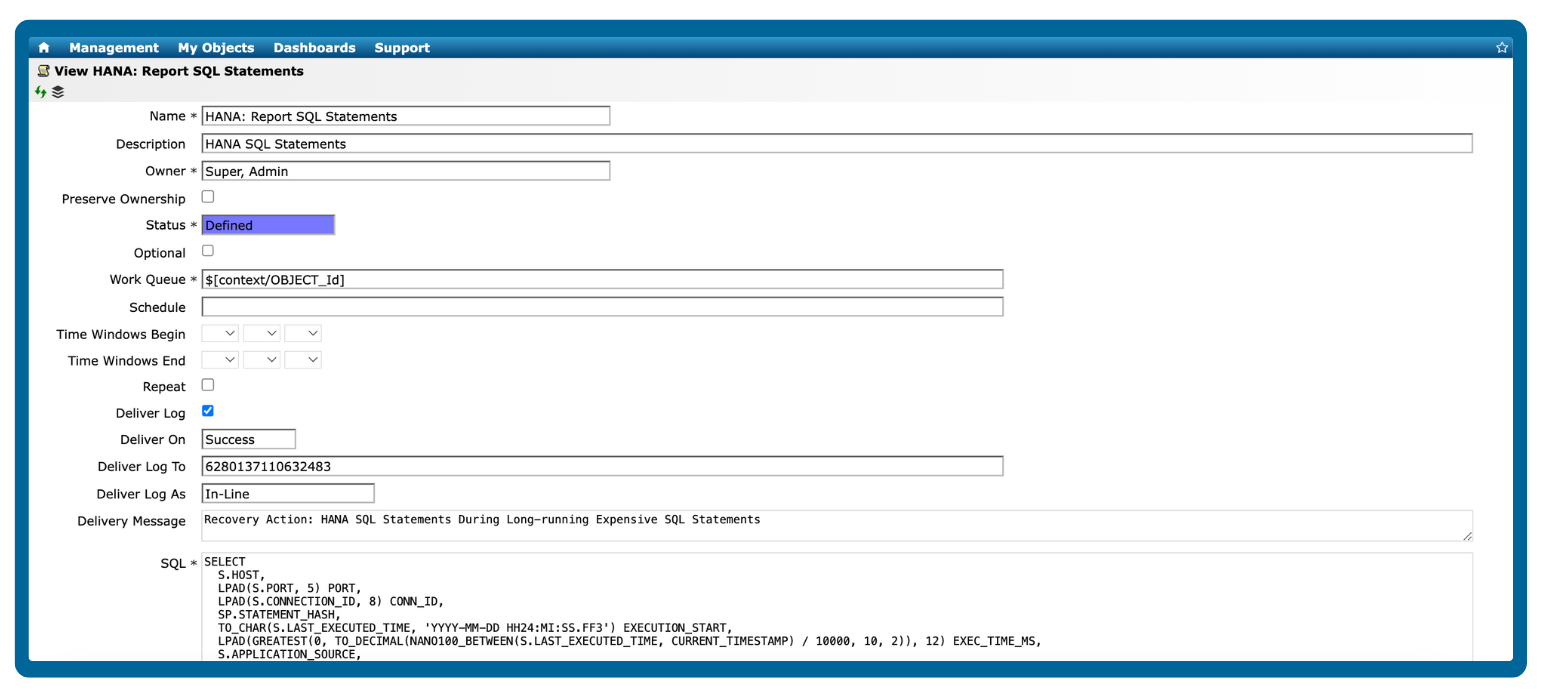
A database may be performing poorly if it exhibits slow queries, high resource usage, or frequent errors, which can impact applications and end-user experience.
Key indicators include:
-
Slow query execution: Queries take longer than usual to return results.
-
High CPU or memory usage: Consistently high resource consumption on the database server.
-
Excessive I/O or disk latency: Delays in reading or writing data to storage.
-
Connection issues: Frequent timeouts, failed connections, or blocked sessions.
-
Transaction delays or deadlocks: Conflicts that prevent transactions from completing.
-
Error logs: Increased frequency of warnings or critical errors in database logs.
Monitoring these metrics over time, correlating them with application performance, and setting thresholds for alerts can help you detect poor performance before it affects end users.