Infrastructure Monitoring and Observability Solution
Simplify infrastructure monitoring and management with IT-Conductor's unified monitoring capability and advanced observability features. Quickly resolve issues and take charge of your IT infrastructure today!
Start managing your IT infrastructure almost instantly with IT-Conductor's agentless monitoring framework. Learn More →
Manage end-to-end IT infrastructure from a single platform
Monitor servers, databases, and other compute resources both on-premises and in the cloud, all from a single pane of glass.
Ensure optimal application performance with continuous monitoring and advanced observability for peak efficiency.
Monitor the health, performance, and availability of cloud infrastructure across AWS, Azure, GCP, and other cloud service providers.
Monitor DBMS health, track query performance, and ensure data integrity to support your critical business operations.
Deliver exceptional user experiences by monitoring user interactions and understanding user behavior to drive continuous improvement.
Proactively monitor and manage resources and detect failures to keep your servers healthy and maintain system reliability.
Gain real-time visibility into your VMware environment, enabling you to proactively identify and resolve issues before they impact your business.
Identify and troubleshoot network issues, optimize performance, and ensure reliable connectivity to maintain a resilient and secure network.
Detect security threats, respond to incidents promptly, and safeguard your data and infrastructure against potential security breaches.
Monitor storage usage, identify storage issues, and manage capacity effectively to maintain peak system performance across the entire IT infrastructure.
Designed for complex and hybrid infrastructure
Achieve operational clarity and confidence when managing complex, large-scale IT across on-premises and multi-cloud environments.
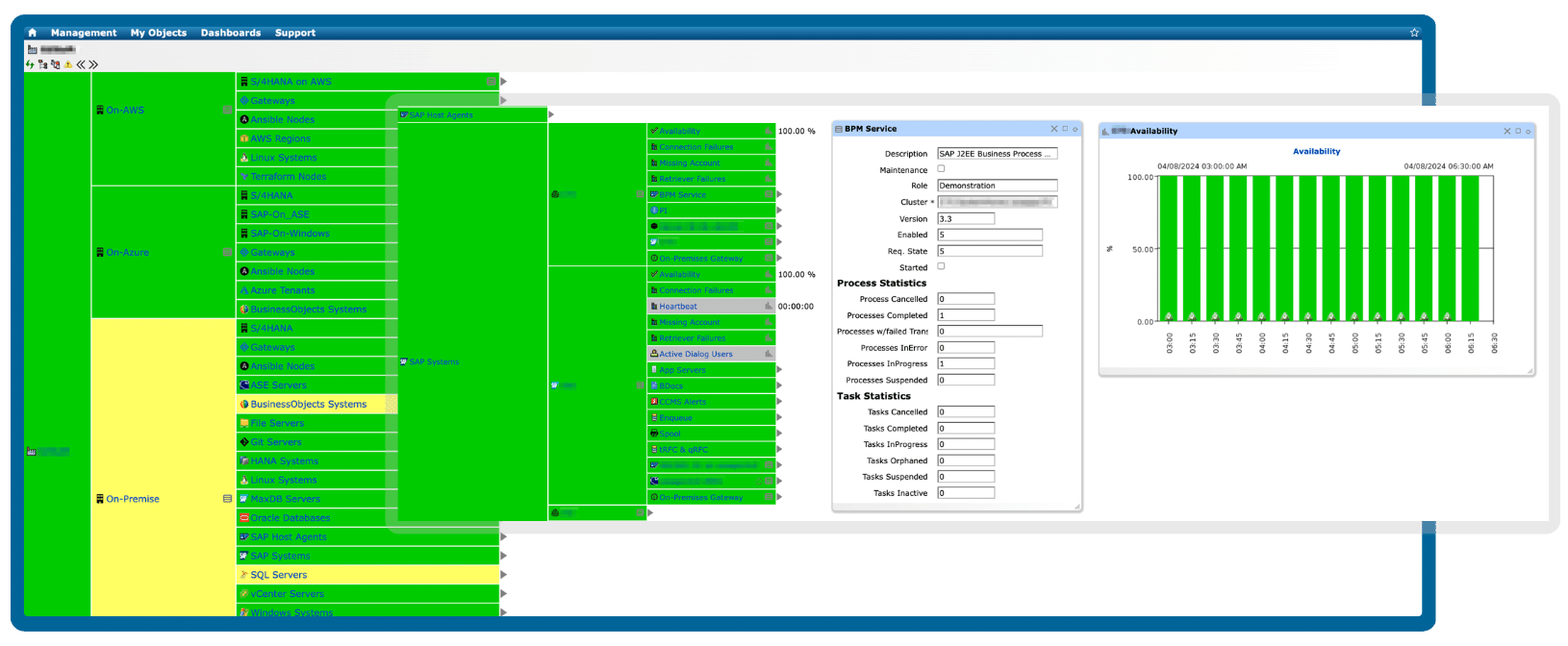
Customize alerts & notifications for proactive monitoring
Receive timely notifications on critical events to stay on top of high-priority incidents.
Customize alert settings to ensure only relevant information reaches the right teams, cutting through the noise and maximizing performance.
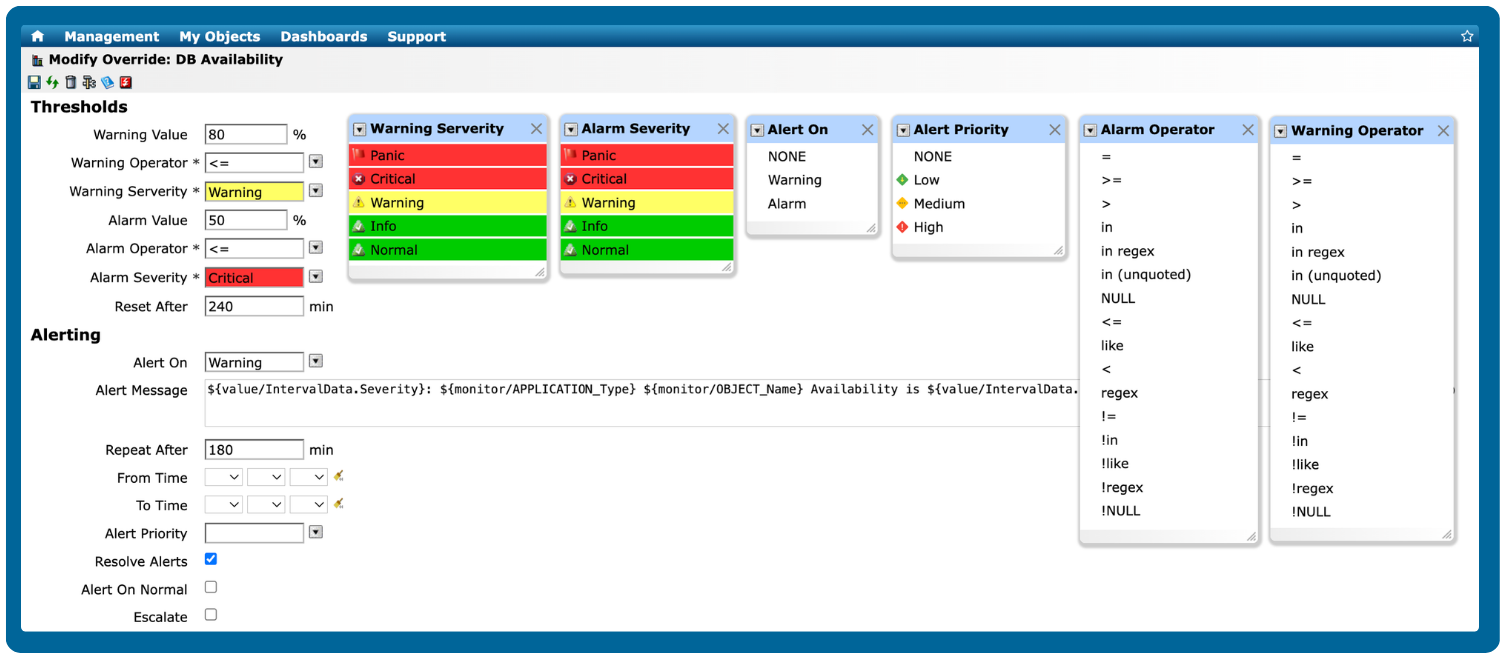
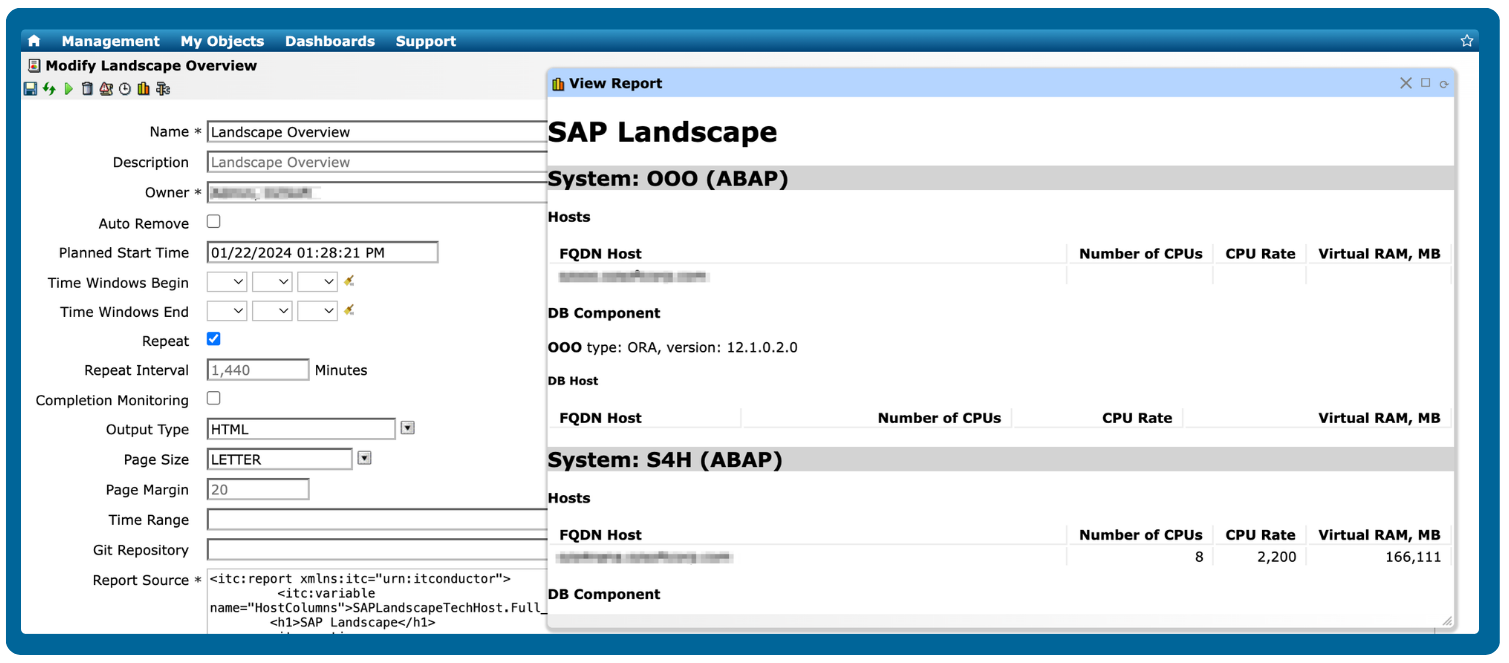
Enhance visibility with integrated dashboards and reporting
Go beyond alerts and leverage IT-Conductor's highly flexible dashboard and reporting features to send customized reports or perform root cause analysis.
Gain valuable insights into key performance indicators (KPIs) and drive informed decision-making with real-time, continuously updated data.
Improve troubleshooting with application-infrastructure correlation
IT-Conductor simplifies the correlation between applications and infrastructure components to better visualize their connections and dependencies.
Utilize time-synchronized data to better visualize context and mapping between applications and infrastructure. This enhanced visibility allows for more efficient troubleshooting and optimization, improving system performance and reliability.

Design, build, and deploy resources at cloud speed
Streamline resource provisioning and deployment processes to scale effortlessly, adapt quickly, and stay ahead.
Trusted by leading brands worldwide

IT-Conductor continued to work seamlessly with Coats during the COVID-19 pandemic to support its mission of delivering critical textiles needed for personal protection equipment manufacturing, such as face masks and hospital wear, especially when remote management was the mode of operation from a global hybrid workforce.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is infrastructure monitoring?
Infrastructure monitoring is the process of tracking, measuring, and analyzing the performance, availability, and health of IT infrastructure components, including servers, storage, databases, network, and other cloud resources. It helps IT teams detect issues early, maintain uptime, and ensure optimal performance for applications and business services.
What is the difference between monitoring and observability in the context of IT infrastructure?
Monitoring involves collecting predefined metrics and logs from servers, networks, storage, and applications to detect known issues and trigger alerts. It tells you that a problem exists, but often doesn’t provide the full context for why it happened.
Observability, on the other hand, is about understanding the internal state of systems based on the data they produce. By combining metrics, logs, traces, and events, observability enables IT teams to analyze, diagnose, and predict issues, even those that were previously unknown.
How does infrastructure monitoring work?
Agentless infrastructure monitoring collects performance and health data from servers, networks, storage, and applications without installing software agents on each device. Instead, it uses standard protocols and APIs, such as SNMP, WMI, SSH, REST, or cloud provider APIs, to pull metrics, logs, and status information remotely.
IT-Conductor leverages agentless monitoring to correlate infrastructure metrics with application and business process performance, providing end-to-end visibility and automated remediation across on-prem, cloud, and hybrid environments.
What are the best practices for setting up alerts and thresholds in infrastructure monitoring?
Effective alerting ensures your IT team responds to issues promptly without being overwhelmed by noise.
Here are some best practices that you can follow:
-
Define meaningful thresholds: Set thresholds based on historical performance and business impact rather than default values. For example, trigger alerts when CPU usage consistently exceeds 80% for 10 minutes, not on a single spike.
-
Use dynamic baselines and anomaly detection: Leverage automated tools to detect deviations from normal behavior instead of static thresholds.
-
Prioritize alerts: Categorize alerts by severity (critical, warning, informational) so your team can focus on high-impact issues first.
-
Correlate alerts across systems: Avoid alert storms by grouping related events across servers, networks, and applications.
-
Automate remediation where possible: Integrate alerts with automated actions, like restarting services or scaling resources, to reduce downtime.
-
Review and adjust regularly: Continuously analyze alert patterns to reduce false positives and improve effectiveness.
How do I secure monitoring data in transit and at rest?
Securing monitoring data is critical to protect sensitive information and maintain compliance.
Best practices include:
-
Encryption in transit: Use protocols like TLS/SSL to encrypt all data transmitted between monitored systems, cloud services, and your monitoring platform.
-
Encryption at rest: Store metrics, logs, and traces in encrypted databases or storage systems using strong encryption standards (e.g., AES-256).
-
Access control and authentication: Restrict access to monitoring data with role-based access control (RBAC), multi-factor authentication (MFA), and secure API keys or service principals.
-
Audit and logging: Maintain logs of who accessed monitoring data and when, helping detect unauthorized access.
-
Secure network connections: Use VPNs or private endpoints when connecting to cloud monitoring APIs or hybrid environments.