Continuous monitoring plays a critical role in ensuring the optimal performance of an SAP system. With this approach, you can identify and address issues before they impact business operations. It can help prevent system downtime, data loss, or other issues that could impact the smooth running of a business.
Moreover, continuous monitoring can provide valuable insights into user behavior and system usage, enabling organizations to optimize SAP systems for improved performance and productivity. By analyzing user activity and resource utilization, companies can identify areas where training or process improvements may be needed, helping to streamline workflows and increase efficiency. This can lead to cost savings and a competitive advantage for organizations that can run their SAP systems more effectively and efficiently than competitors.
In this blog post, we will discuss the key areas to continuously monitor for efficient SAP performance. Regularly monitoring these critical areas will ensure a stable and reliable SAP system performance.
Table of Contents
1. System Health Metrics
2. System Performance Metrics
3. Database Performance Metrics
4. System Logs
5. User Activity and Security
6. Batch Jobs
7. Interface
8. Short dumps
9. Change Management
10. Backup and Recovery
Read Related Post:
SAP Monitoring Tools Overview (Updated May 2022)
1. System Health Metrics
System health comprises system availability, system responsiveness, and resource utilization. Monitoring these key areas can help ensure optimal system performance.
To achieve this, you need to check the system status and uptime, as well as monitor the system response time. Regular monitoring of the system's health can help identify potential problems early and take corrective action before they escalate.
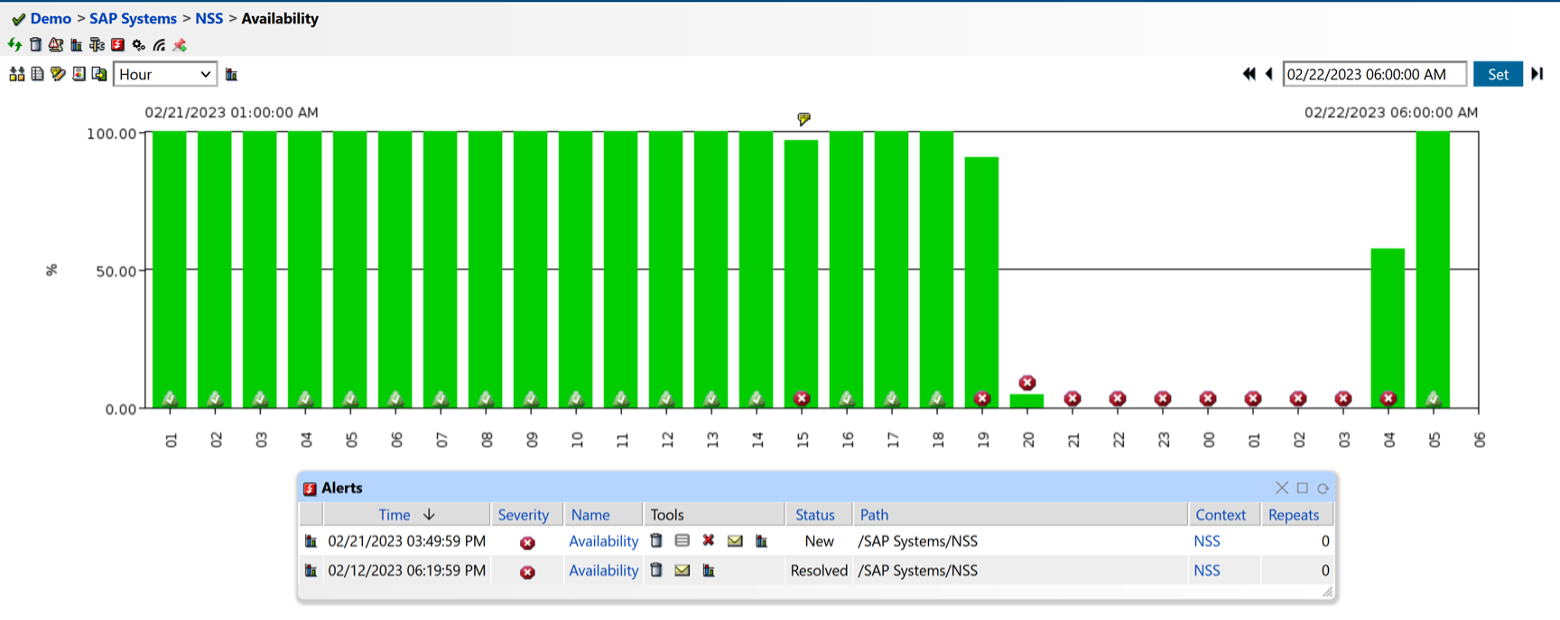
Figure 1: System Availability
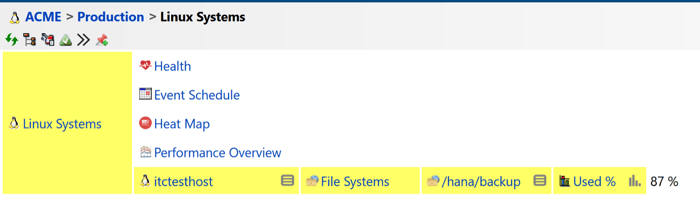
Figure 2: Disk Utilization
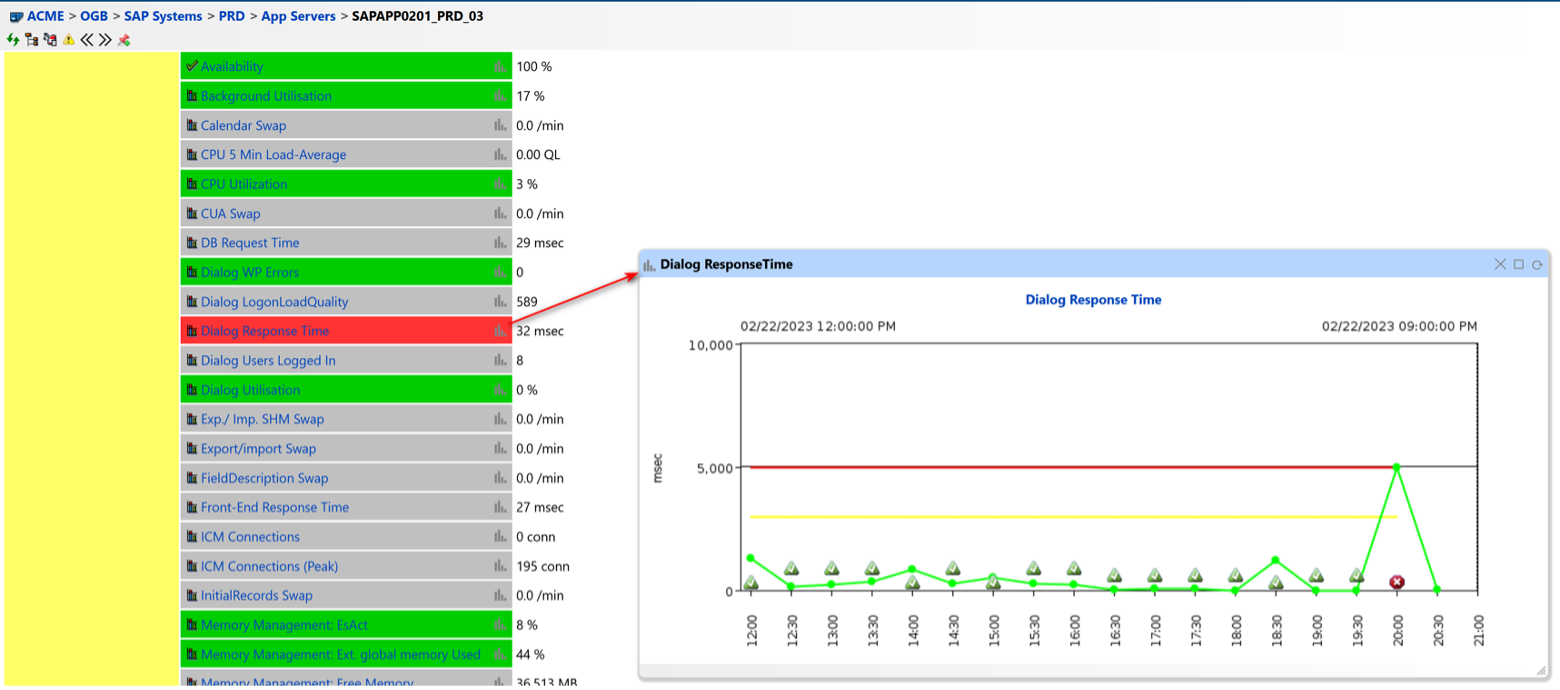
Figure 3: Dialog Response Time
The performance of your SAP system is critical to its operation. Monitoring the system performance can help to identify any bottlenecks or issues that could affect system performance. This includes monitoring CPU usage, memory usage, disk I/O, network I/O, and other performance metrics. Monitoring the CPU usage, memory usage, and disk usage can help detect when the system is under stress and when the disk is nearing capacity.
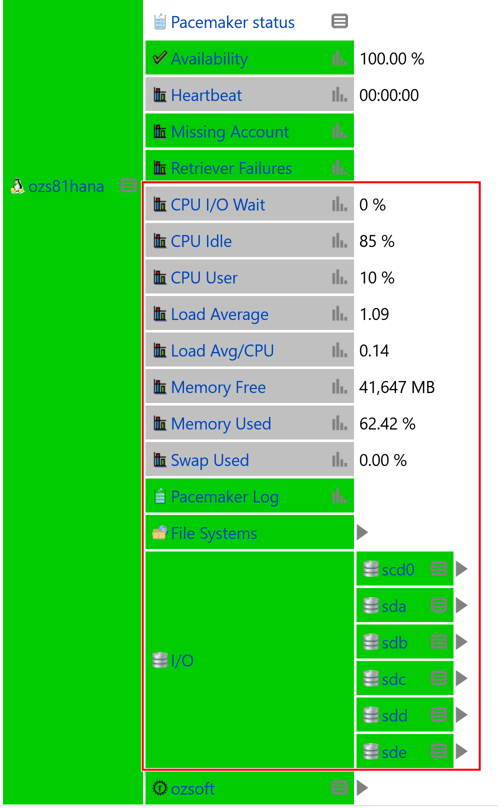 Figure 4: Resource Utilization
Figure 4: Resource Utilization
Monitoring SAP database performance, including database size, table size, and indexing, can help you optimize database performance and improve system response times. Continuous database monitoring is essential to ensure the system is meeting performance targets.

Figure 5: Database Performance Monitoring
Read Related Post:
Monitoring SAP Data Services with IT-Conductor
4. System Logs
Monitoring system logs can help identify system errors, warnings, and other important events. It is useful for troubleshooting errors or issues that may impact system stability and performance. For example, errors related to failed database connections canceled transactions or user locks.
Continuous monitoring of SAP system logs can help to detect errors that can potentially cause system downtime.
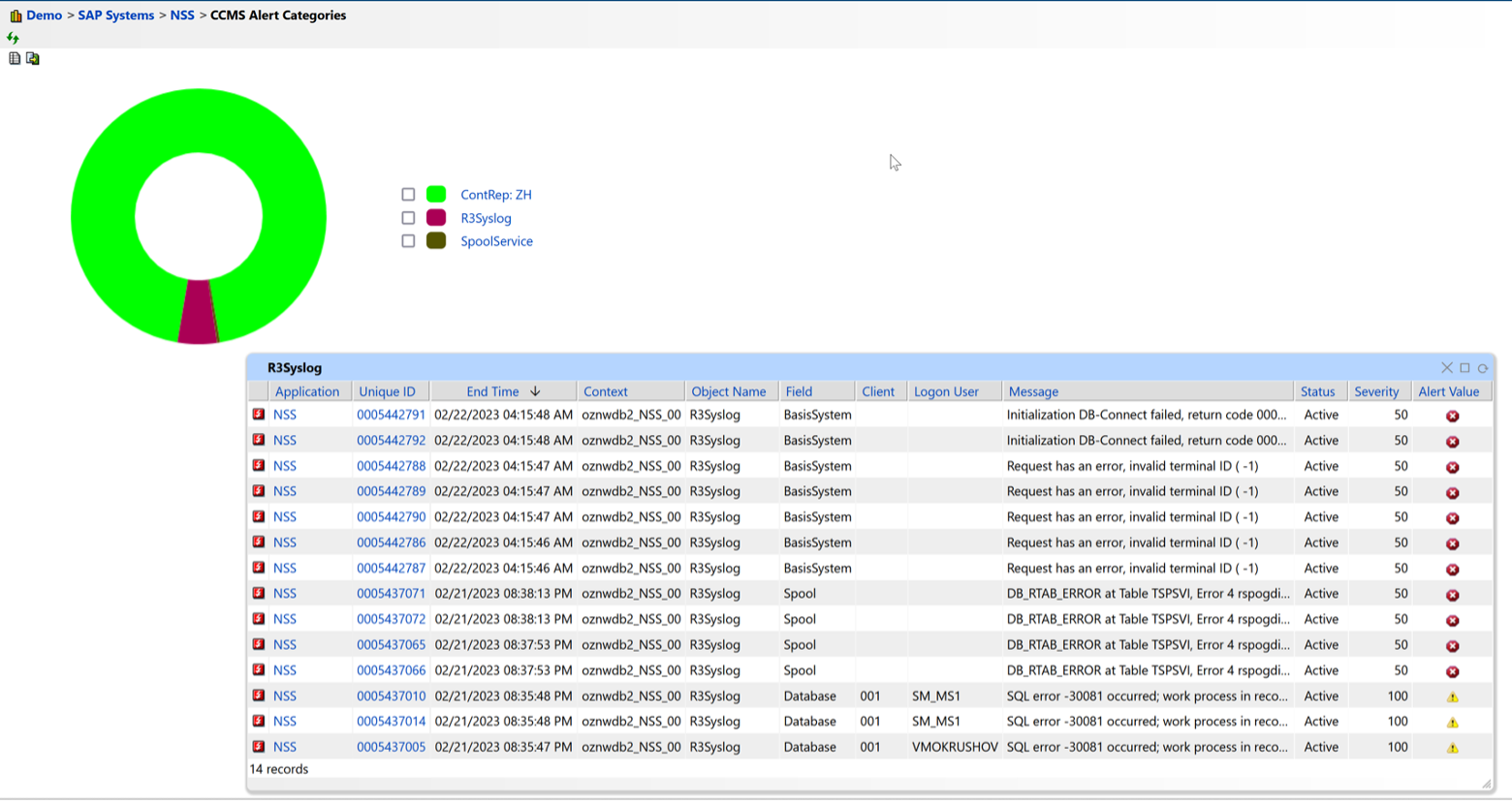
Figure 6: Syslog Monitoring
Read Related Post:
Auditing HANA Security via IT-Conductor Syslog Monitoring
5. User Activity and Security
User activity monitoring such as user logins and other user-related metrics plays an important role in the security and integrity of your SAP system. Through the continuous monitoring of user activities, you can verify that users are not accessing or modifying data for which they are not authorized. This can help to demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements and ensure that your organization is adhering to internal policies and procedures.
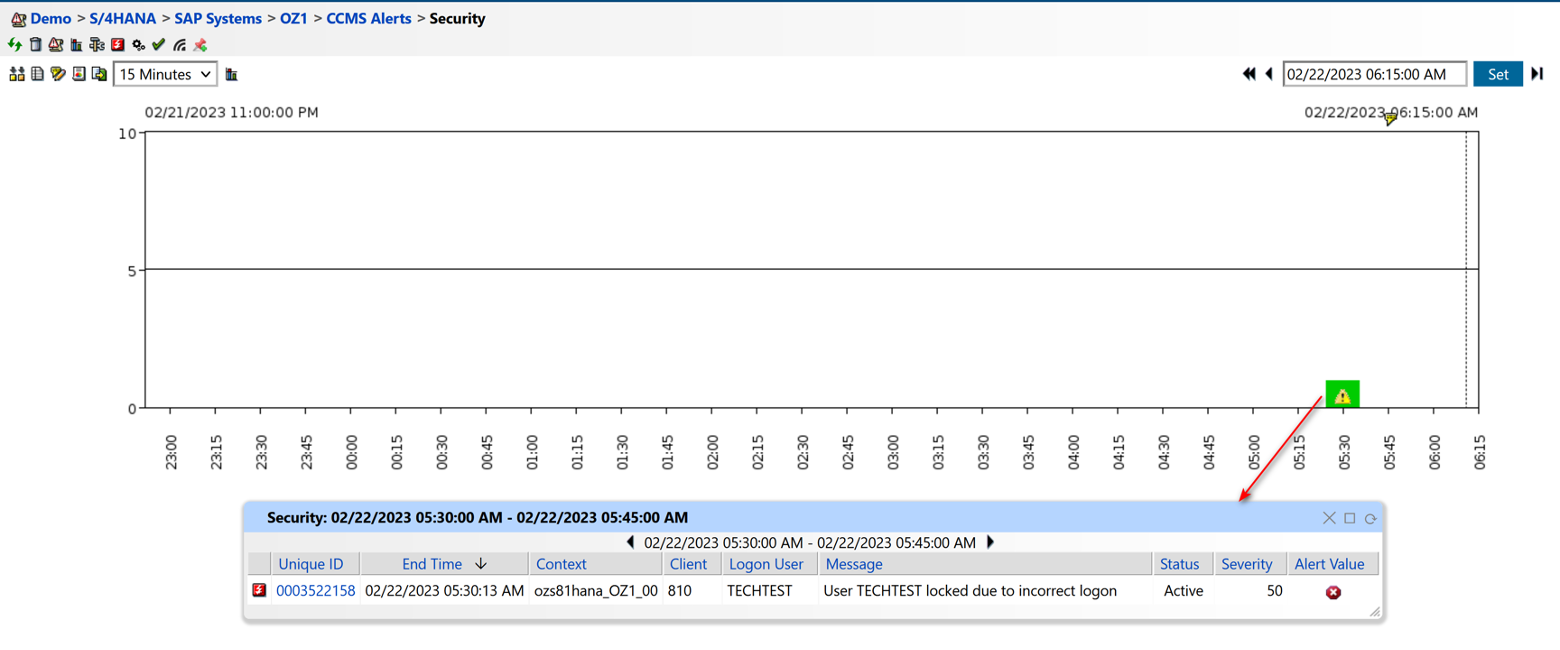
Figure 7: User Activity Monitoring
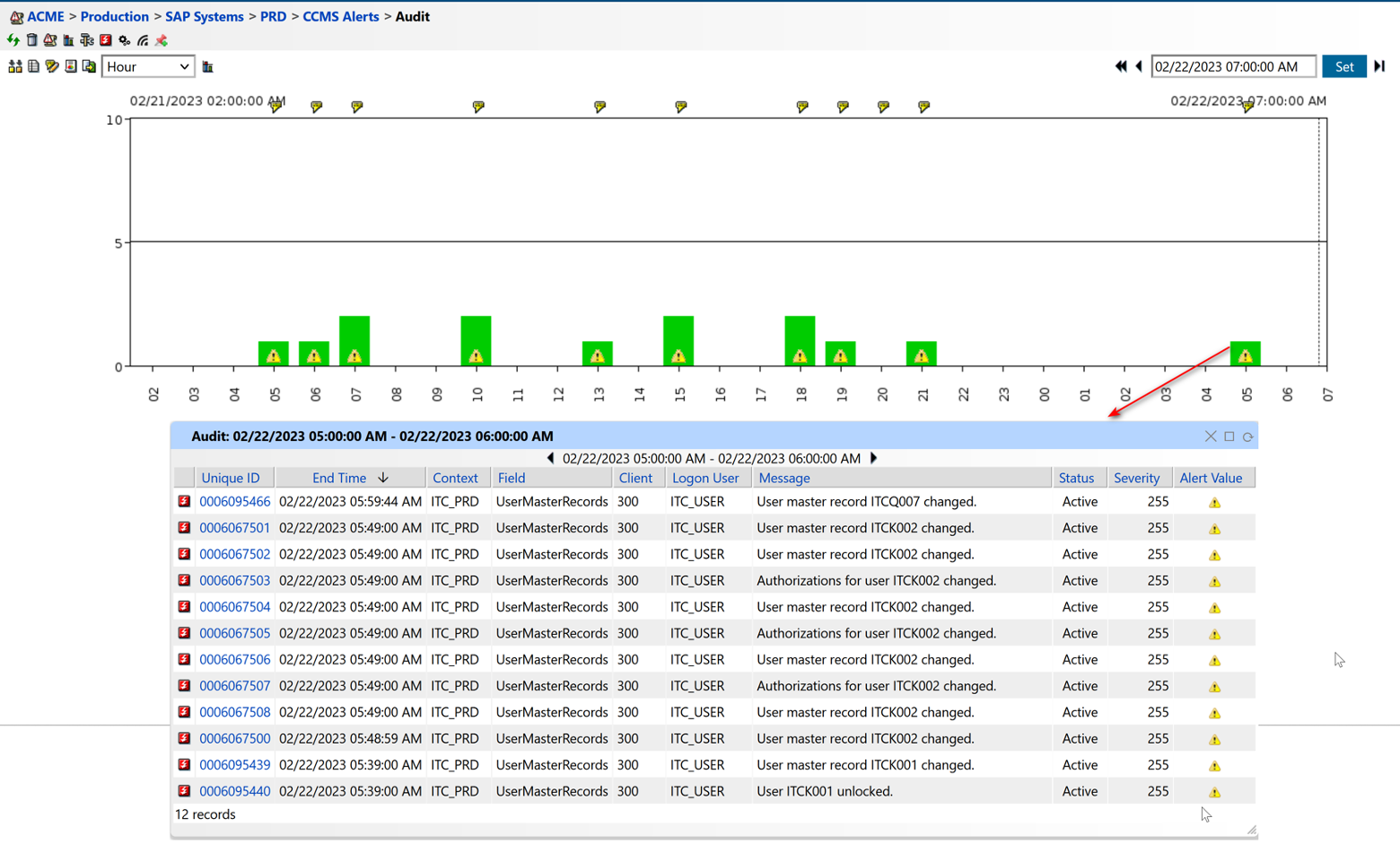
Figure 8: Audit Log Monitoring
6. Batch Jobs
Monitoring scheduled jobs and background processes ensure that they complete successfully and do not impact system performance. This includes monitoring job logs, checking job status, and verifying that jobs are successfully completed.
By monitoring the completion of jobs and promptly addressing any job failures, organizations can ensure the smooth running of critical business processes.
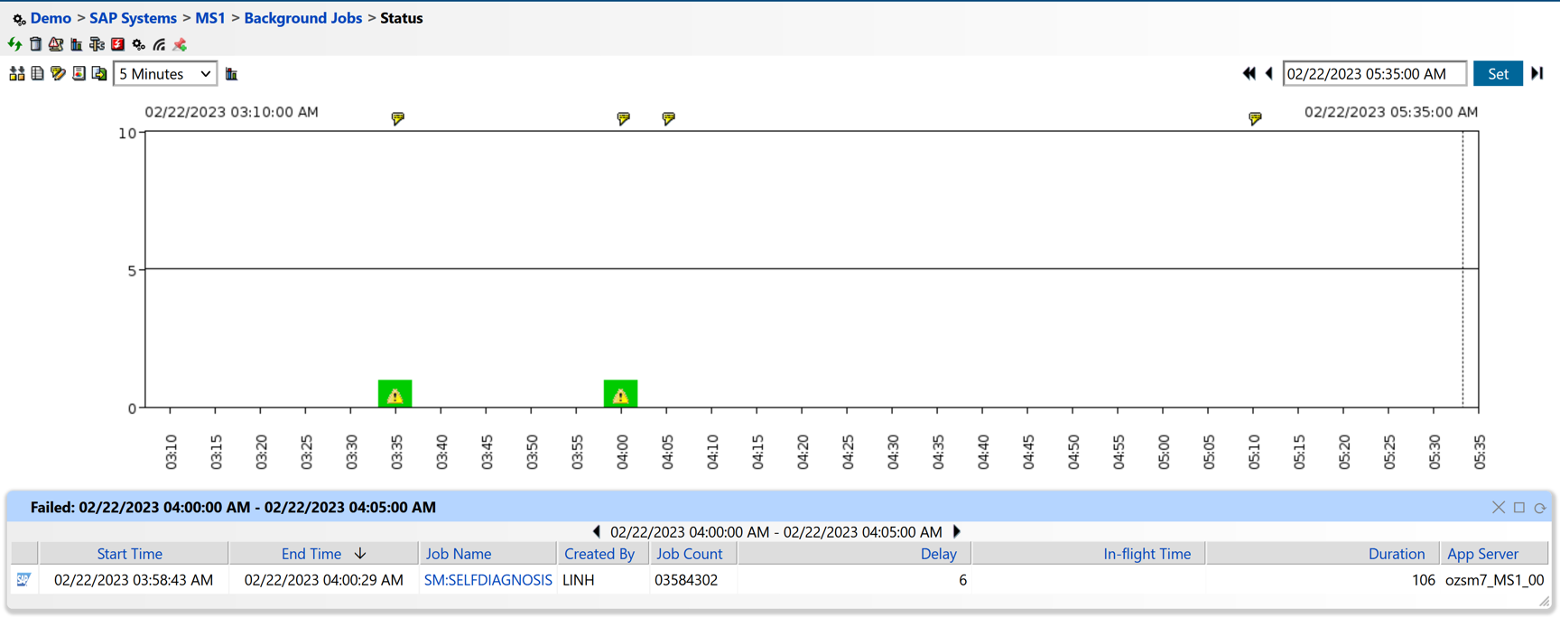
Figure 9: Batch Job Monitoring
7. Interface
Interfaces are critical to exchanging data between your SAP system and other systems. Monitoring the status of interfaces and ensuring that data is being exchanged correctly between systems will help prevent data loss and improve system performance.
This includes monitoring interface logs, checking the status of interface jobs, and verifying that data is being exchanged successfully.
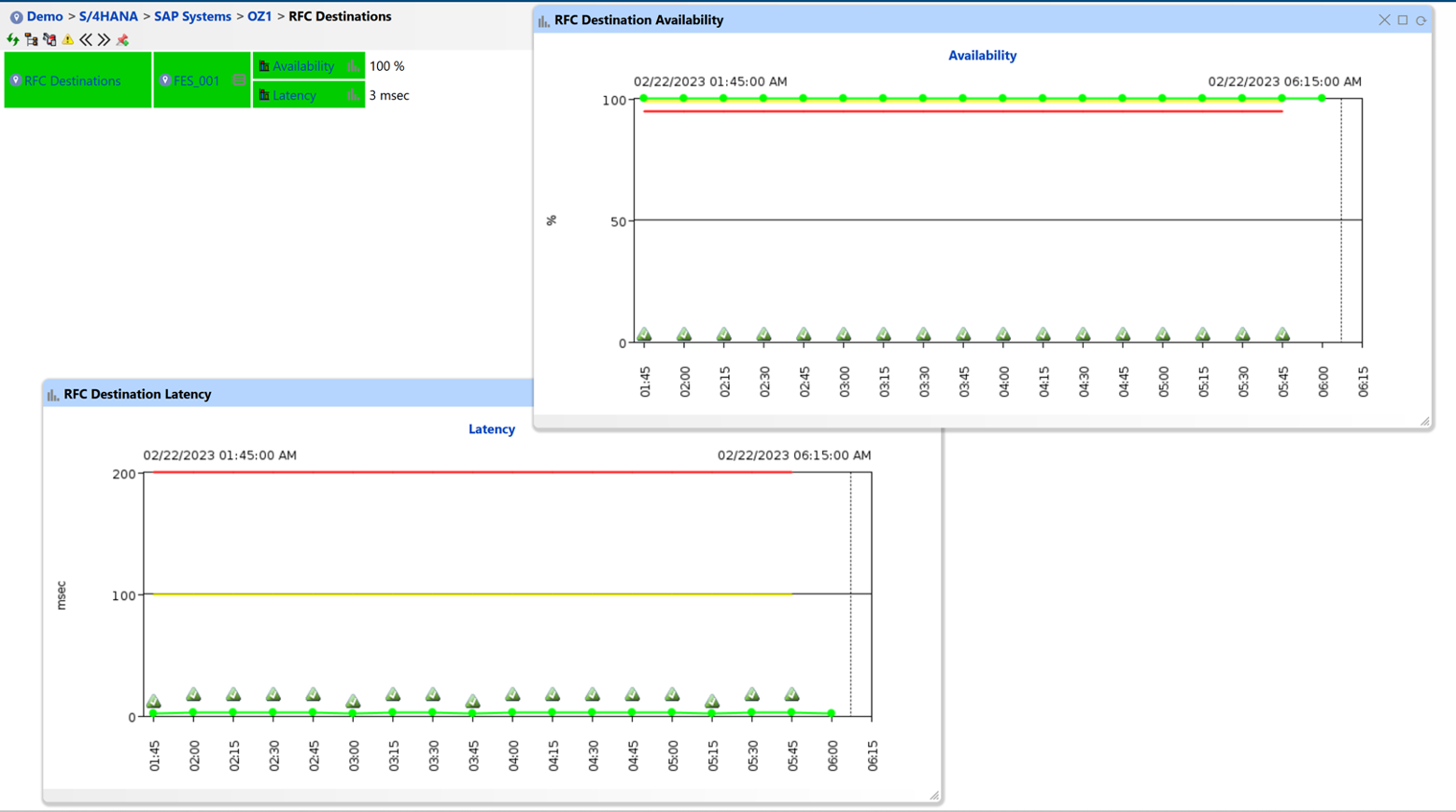
Figure 10: RFC Destination Monitoring
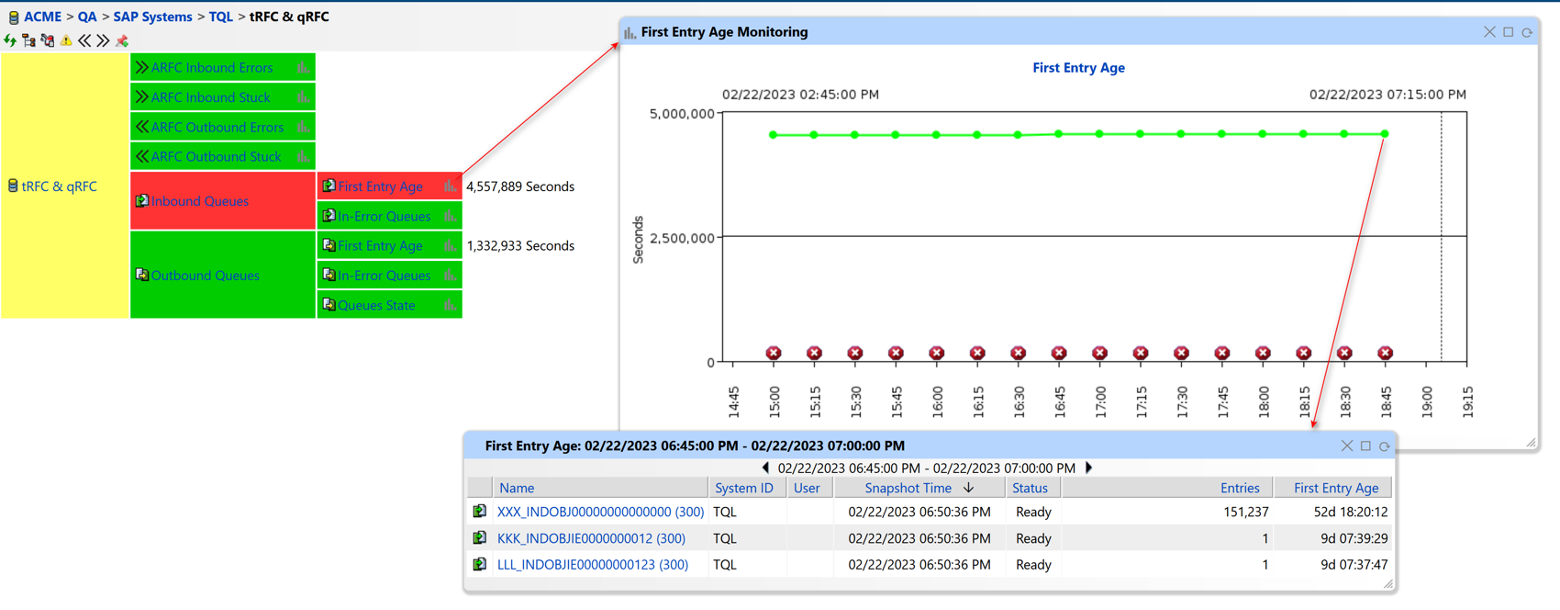
Figure 11: tRFC and qRFC Monitoring
8. Short dumps
ABAP dumps are an important aspect of continuous SAP monitoring because they provide critical information about system errors and can help identify potential performance issues.
By monitoring ABAP dumps, system administrators can quickly identify and address errors before they lead to system downtime or data loss. Additionally, analyzing ABAP dumps can help pinpoint the root cause of system issues and enable more effective problem resolution.
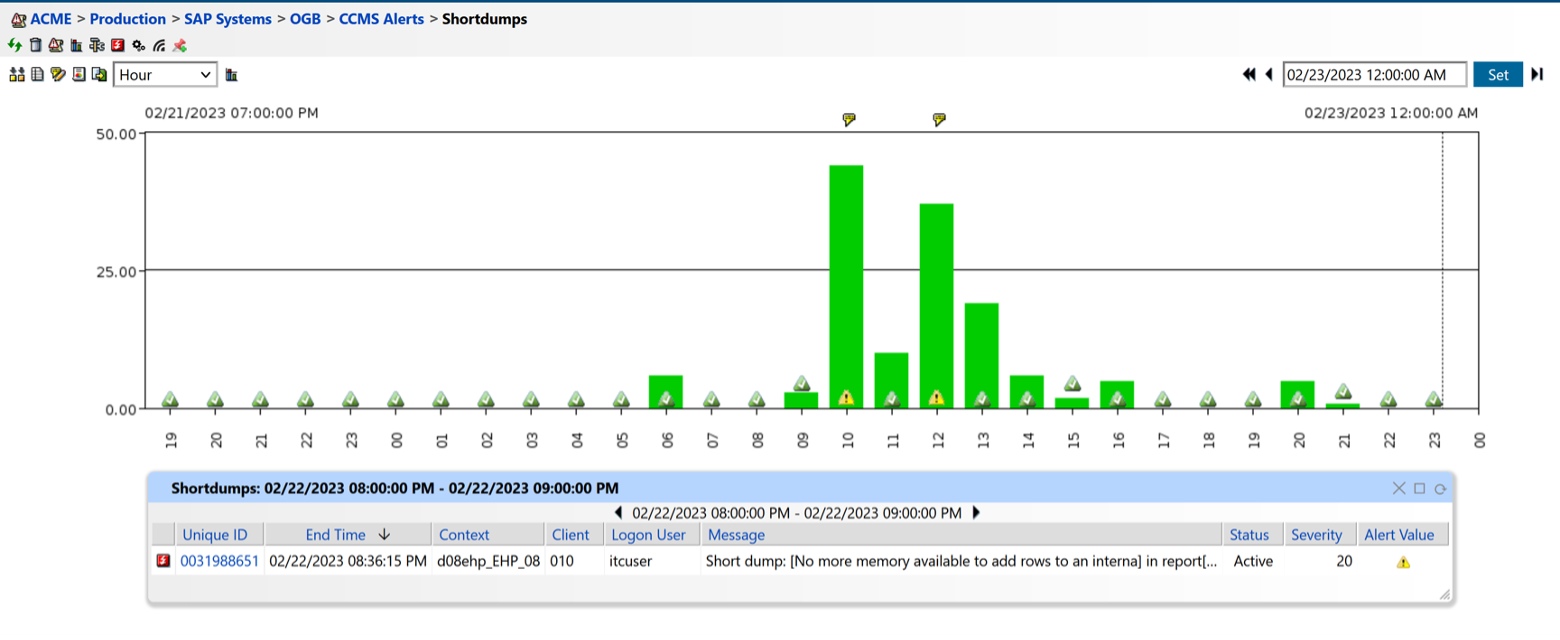
Figure 12: Shortdumps Monitoring
9. Change Management
Monitoring the configuration, customization, and development changes in your SAP system can help to prevent unauthorized changes and keep the system in a stable and secure state. It also helps in maintaining compliance with industry standards and regulations.
Effective change management monitoring can help avoid costly mistakes and minimize downtime, leading to better overall system performance and stability.
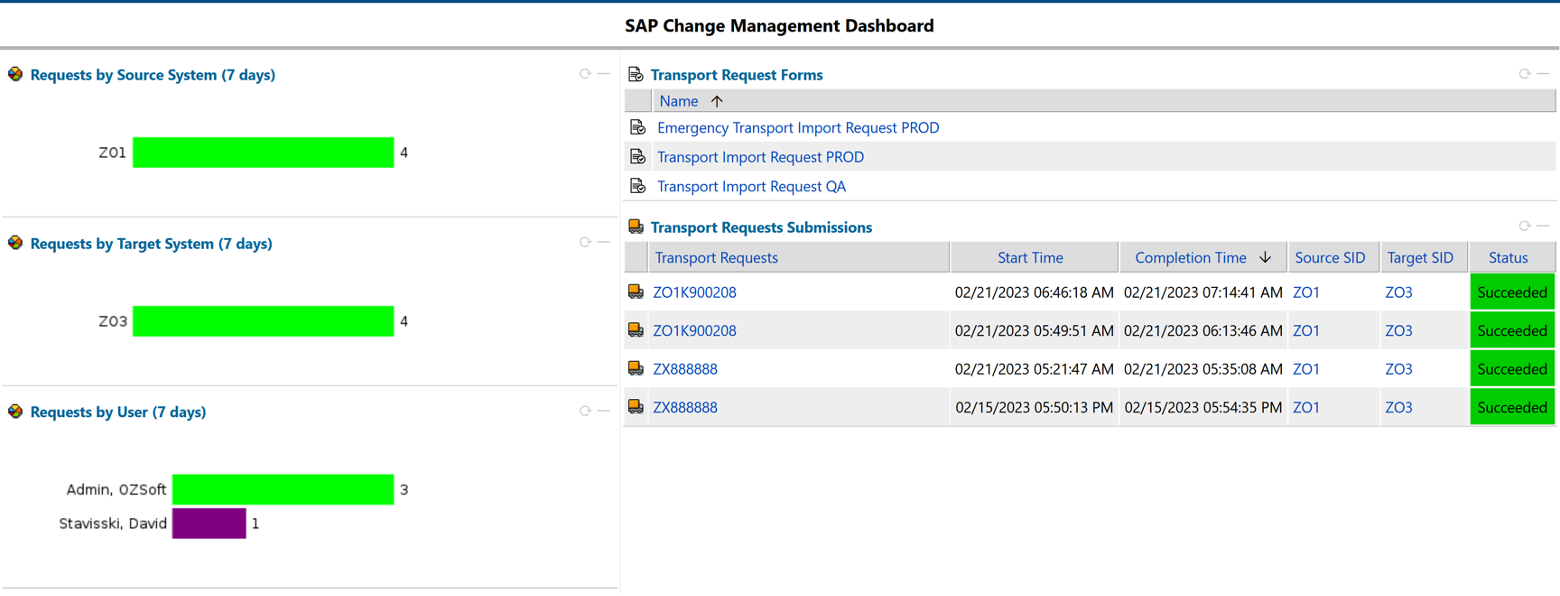
Figure 13: Change Management Monitoring
10. Backup and Recovery
The final area to monitor is backup and recovery. Monitoring backup and recovery processes ensure data is backed up regularly and can be successfully restored in case of system failure or data loss. Regularly testing backups, and identifying and fixing any issues can help you protect against data loss and ensure business continuity.
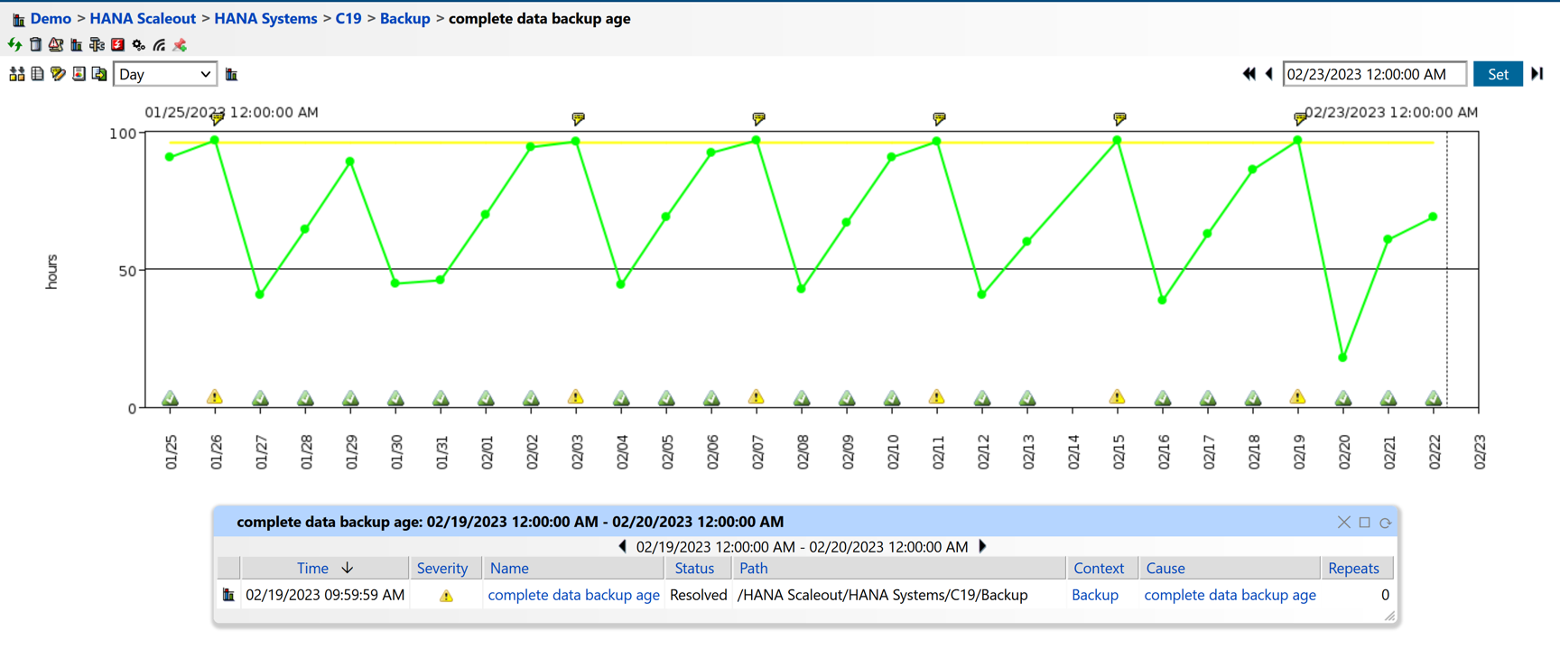
Figure 14: Backup Monitoring
Key Takeaway
In summary, regular monitoring is crucial for maintaining the stability, performance, and security of your SAP system. By consistently monitoring the top 10 areas mentioned, potential issues can be proactively identified and resolved before they escalate and negatively impact business operations.
IT-Conductor provides an ideal solution that covers all 10 areas requiring continuous monitoring, management, and intelligent automation.
